deotadepante
Deoxyribonucleic acid (English) [ IPA: [Deoxyribonucleic] ˈæsəd ASM: ডিঅ’ক্সিৰিবনিউক্লিক এচিড]
Contributed by: Pankaj Borah (পঙ্কজ বৰা) on 2008-07-08
Deoxyribonucleic acid (English) [ IPA: [Deoxyribonucleic] ˈæsəd ASM: ডিঅ’ক্সিৰিবনিউক্লিক এচিড]
Contributed by: Pankaj Borah (পঙ্কজ বৰা) on 2008-07-08
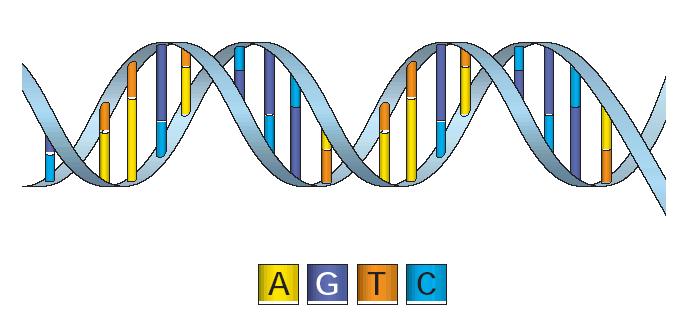
1. (Material Noun-Neuter) Deoxyribonucleic acid, the genetic material in the nuclei of all cells. Chemically it is a polymer of deoxyribonucleotides; the purine bases adenine and guanine, and the pyrimidine bases thymidine and cytidine, linked to deoxyribose phosphate. The sugar-phosphates form a double-stranded helix, with the bases paired internally.DNA is often compared to a set of blueprints or a recipe, since it contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells, such as proteins and RNA molecules.DNA was first isolated by the Swiss physician Friedrich Miescher who, in 1869, discovered a microscopic substance in the pus of discarded surgical bandages. In 1953, based on X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin and the information that the bases were paired, James D. Watson and Francis Crick suggested what is now accepted as the first accurate model of DNA double helical structure. ডিঅক্সিৰাইব`নিউক্লিক এচিদ বা ডিএনএ সকলো কোষৰ কোষকেন্দ্ৰত থকা আনুবংশীয় উপাদান | ৰাসায়নিক ভাৱে ই ডিঅক্সিৰাইব`নিউক্লিঅ’টাইদ (এডিনিন, থাইমিন, গুৱানিন , চাইট`চিন),ৰ বহুযোগী যৌগ যিবিলাক ডিঅক্সিৰাইব`ফছফেটৰ দ্বাৰা লগ লাগি থাকে|চুইচ্ বিজ্ঞানী ফ্ৰেডেৰিক মাইছাৰে ১৮৬৯ চনত প্ৰথম ইয়াক আৱিষ্কাৰ কৰিছিল | ৰ`জেলিন ফ্ৰেঙ্কলিনৰ ৰঞ্জন ৰশ্মি অপৱৰ্তন পৰীক্ষাৰ ওপৰত ভিত্তি কৰি ১৯৫৩ চনত ফ্ৰাঞ্চিচ ক্ৰিক আৰু জে ডি ৱাটছনে ডিএনএৰ দুদলীয়া সৰ্পিল আৰ্হি প্ৰকাশ কৰে | ইয়াৰ লগে লগে আনৱিক জীৱবিজ্ঞানৰ নতুন যুগৰ সূচনা হয় | ক্ৰিক আৰু ৱাটছনে যুটীয়া ভাৱে চিকিৎসা বিজ্ঞানৰ নবেল বঁটা লাভ কৰে |